Non-tech stakeholders often come from business, marketing, finance, operations, or leadership positions. Their core strength is understanding customers, market trends, user needs, and business goals—not code.
But in most modern businesses, software plays a major role. From customer apps to internal tools, from automation to dashboards, from AI integrations to cloud platforms—almost every product depends on technology. This makes collaboration between tech teams and non-tech teams absolutely essential.
However, challenges arise because:
- Technical processes seem complex
- Requirements change often
- Timelines shift
- Priorities need alignment
- Communication gaps happen
- Understanding progress becomes difficult
This is where Agile Development shines. It's a Software Development Methodology built specifically to improve communication, reduce confusion, and make the entire development process transparent. Instead of working like a black box, Agile works like a series of clear, small steps—where stakeholders are involved at every stage.
What Is Agile Development?
If you’re a non-tech stakeholder, here’s the simplest way to understand Agile:
Agile = Work in small steps + get continuous feedback + improve continuously
Instead of planning everything for months and delivering at the end (which is risky and slow), Agile breaks the project into smaller chunks called sprints. Each sprint lasts about 1–2 weeks, and the team focuses on building specific features within that time.
This method ensures:
- Faster delivery
- Better quality
- Fewer misunderstandings
- Easier course correction
- Better collaboration with stakeholders
Compared to older methods like Waterfall, which require creating the whole product before testing, Agile software development gives stakeholders visibility from the very beginning.
You see progress every 1–2 weeks, not after 6 months.
The Key Players in an Agile Team
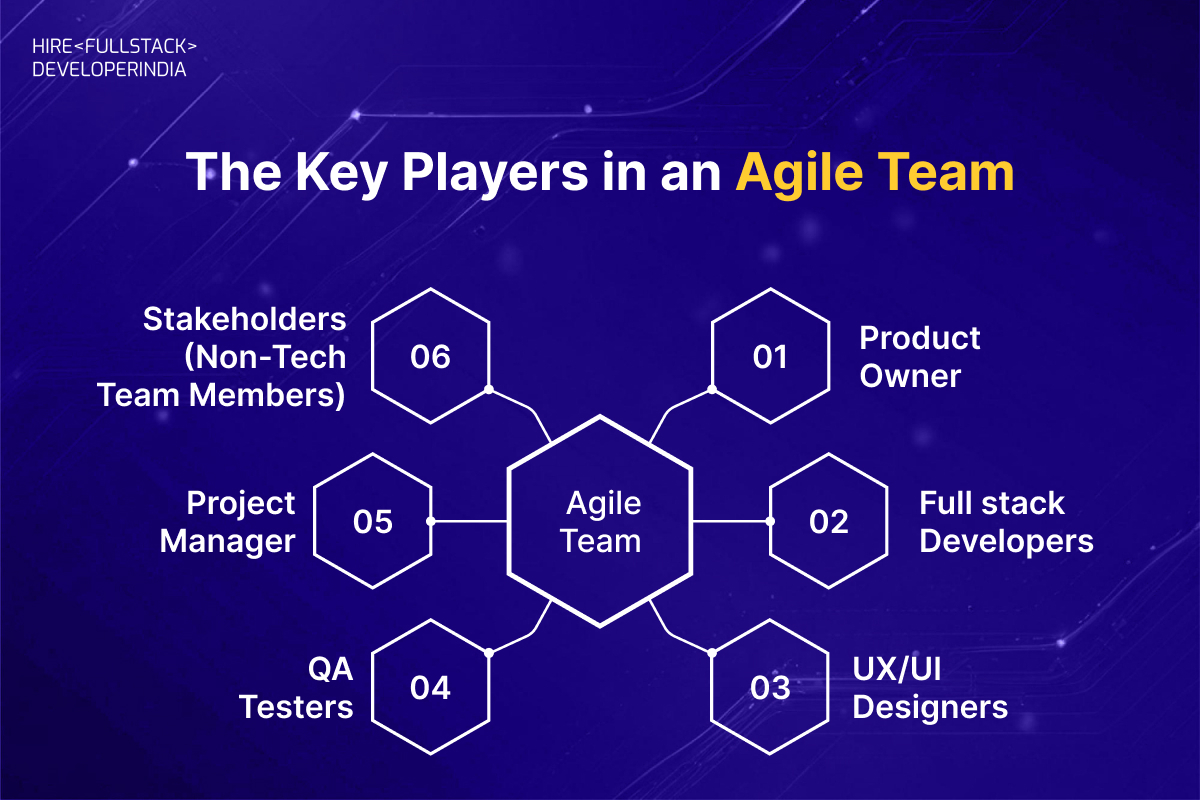
When you’re not from a technical background, it’s easy to feel confused about who does what in a development team. But understanding roles is important because it helps you know whom to talk to, what to expect, and how decisions are made. Here’s a clear explanation of each role in an Agile setup:
1. Product Owner
The Product Owner (PO) is the bridge between business and technology. The Product Owner makes sure the team builds the right thing at the right time. They are responsible for deeply understanding business goals, user needs, and market expectations.
What they do:
- Convert business ideas into clear, actionable tasks
- Prioritize what features should be built first
- Ensure the development team builds things that deliver real value
- Provide clarity when developers or designers need more details
- Make final decisions on what goes into the product
2. Full-Stack Developers
Full-stack developers are the backbone of the application. They work on both the frontend and backend, which gives them a complete understanding of how the entire system works.
Frontend (What users see):
- Buttons, forms, dashboards
- Visual elements
- User interactions on the screen
Backend (What users don’t see):
- Data processing
- Business logic
- Server operations
- Connecting to databases
Why full-stack developers are valuable:
- They work faster because they don’t depend on separate teams
- They can quickly switch between UI and logic
- They ensure the entire system works smoothly end-to-end
3. UX/UI Designers
Designers are responsible for making the product visually appealing, easy to navigate, and user-friendly.
What they create:
- Wireframes (simple sketches of screens)
- Final UI designs
- User flows
- Visual elements like icons and buttons
- Style guides
Why their role is essential:
- They ensure users don’t get confused
- They simplify complex tasks
- They make the product feel smooth and professional
Designers ensure the product is usable, beautiful, and enjoyable.
4. QA Testers (Quality Assurance Team)
Even the best developers can miss small issues. QA testers act as the safety net.
What they do:
- Test every new feature
- Identify bugs or unexpected behaviour
- Ensure the app works on different devices and browsers
- Check performance and speed
- Verify whether the product meets expectations
QA saves the business from risky launches and customer complaints. QA testers make sure the product works perfectly before users touch it.
5. Scrum Master or Project Manager
This role keeps the entire team organized and ensures the Agile process runs smoothly.
What they handle:
- Conduct Agile ceremonies (standups, sprint planning, reviews, retros)
- Remove blockers that slow down the team
- Manage timelines and communication
- Ensure everyone stays aligned with goals
- Protect the team from unnecessary distractions
6. Stakeholders (Non-Tech Team Members)
This includes founders, business owners, marketing teams, sales teams, operations teams, and leadership members.
Their role is NOT passive. They actively help shape the product.
Stakeholders contribute by:
- Providing business insights
- Sharing user needs and market data
- Approving designs and features
- Giving quick feedback on demos
Deciding priorities along with the Product Owner
Agile works best when stakeholders stay involved—not just at the beginning or end, but throughout the project. Stakeholders guide the “why” behind the product, while the tech team builds the “how.”
In Agile Development, all these roles work together like parts of a single machine. No one works in isolation. The entire process depends on collaboration, communication, and continuous feedback. This makes the product stronger, more aligned with business goals, and quicker to deliver.
How Agile and Full-Stack Development Work Together
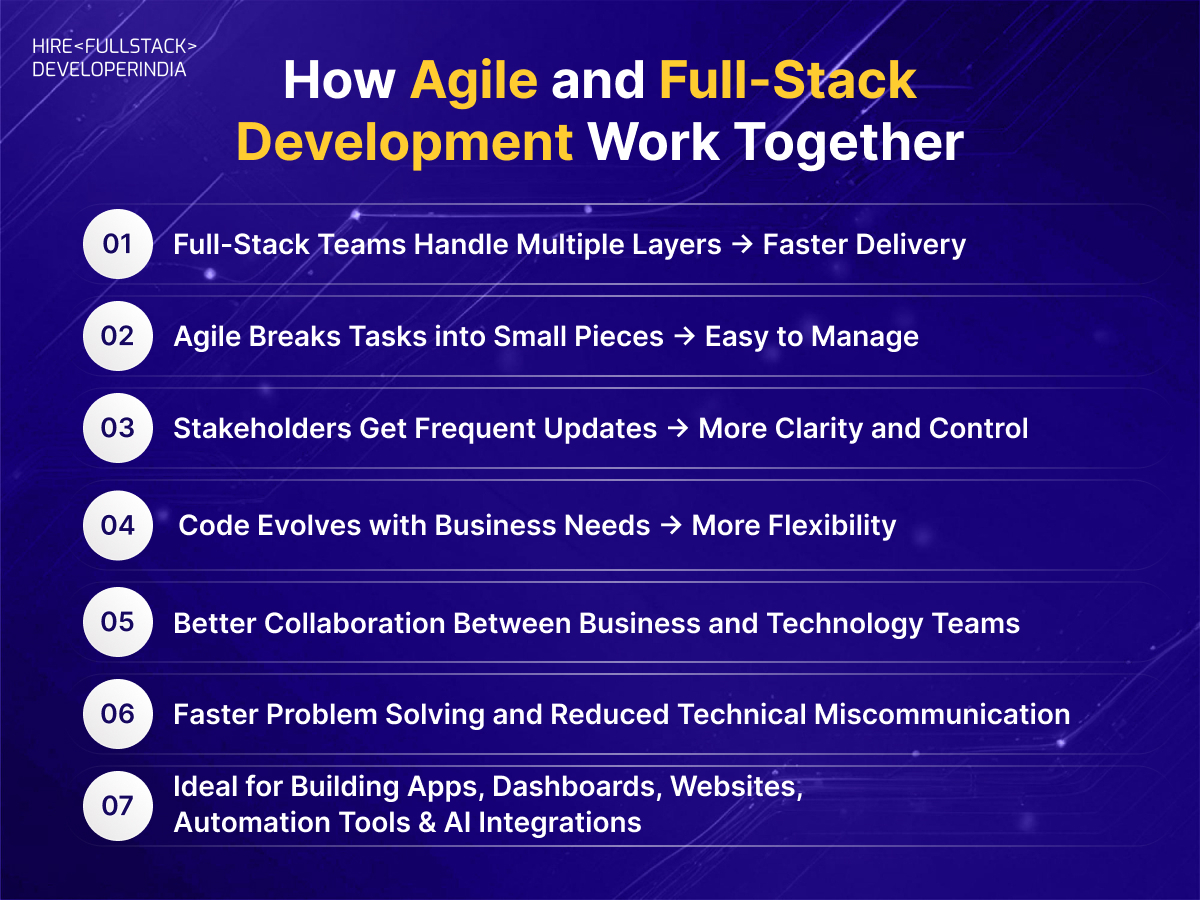
In modern product-building environments, combining Agile Development with full-stack capabilities is one of the most productive approaches. Both support speed, flexibility, and continuous improvement—three things every business needs today.
To understand how they complement each other, let’s break it down.
1. Full-Stack Teams Handle Multiple Layers → Faster Delivery
A full-stack team can build everything—from the user interface to the database—without waiting for separate teams or external dependencies. This reduces delays dramatically.
When paired with Agile software development, this becomes even more powerful, because each sprint delivers a complete, functional piece of the product rather than just one part of it.
Why this matters for businesses:
- You get faster releases
- You see working features sooner
- You reduce dependency bottlenecks
- You get a more predictable development rhythm
This combination improves efficiency across the entire Software Development Methodology.
2. Agile Breaks Tasks into Small Pieces → Easy to Manage
Agile works in short cycles called sprints. Instead of building a massive feature all at once, the work is divided into smaller, manageable chunks.
Full-stack developers thrive in this environment because they can:
- Build the front-end portion of a feature
- Connect the backend logic
- Adjust the database
- Test and refine—all within the same sprint
This allows the team to deliver end-to-end functionality instead of incomplete fragments.
Result: Business teams see progress faster, and the product evolves step by step without overwhelming anyone.
3. Stakeholders Get Frequent Updates → More Clarity and Control
One of the biggest benefits of using Agile with full-stack development is transparency.
Stakeholders don’t have to wait months to see progress. Every sprint includes:
- Demos
- Working screens
- Updated features
- Usability improvements
This gives non-technical teams confidence because they can actually see what is being built—while it’s being built. It also helps them make better decisions, refine ideas, or correct direction early, instead of after the product is completed. Agile Development turns stakeholders from occasional reviewers into active collaborators.
4. Code Evolves with Business Needs → More Flexibility
In traditional development methods, making changes mid-way causes frustration, delays, and extra cost. But Agile is designed to welcome change—even late in the process.
When combined with full-stack capabilities, the flexibility increases because:
- The same developers can work on both UI and backend changes
- Adjustments can be made within the same sprint
- Feature updates don’t require long coordination cycles
- New insights from stakeholders or users can be applied immediately
This adaptability is crucial in a world where customer expectations and market trends change rapidly.
5. Better Collaboration Between Business and Technology Teams
Because Agile is a collaborative Software Development Methodology, it works best when cross-functional teams work together.
Full-stack developers, by nature, understand the end-to-end system. So they can:
- Explain technical constraints more clearly
- Help stakeholders visualize the complete workflow
- Recommend better feature decisions based on system knowledge
- Adapt quickly to new requirements
The Agile mindset + full-stack mindset creates a team that is not just building code, but solving business problems with clarity.
6. Faster Problem Solving and Reduced Technical Miscommunication
Miscommunication happens when teams work in silos. But Agile software development eliminates silos through daily standups, sprint reviews, and continuous feedback loops.
Full-stack developers further reduce miscommunication because:
- One person handles multiple layers of the product
- They understand the bigger picture
- They can troubleshoot faster without waiting for another team
- They take ownership of entire features
This leads to fewer blockers, less confusion, and smoother workflows.
7. Ideal for Building Apps, Dashboards, Websites, Automation Tools & AI Integrations
Whether your business needs:
- A customer mobile app
- A web portal
- A management dashboard
- Automation workflows
- A data-driven product
- AI-powered tools
Agile + full-stack development makes the process: Faster, Clearer, More collaborative, Less risky. This combination ensures technical teams stay aligned with the business vision, while the business stays aligned with what is technically possible.
In Simple Words
- Agile Development = Speed + Communication + Continuous Improvement
- Full-Stack Development = End-to-End Capability + Faster Execution
Together, they create a seamless, flexible, and efficient Software Development Methodology that lets businesses adapt, grow, and innovate without getting stuck in long, rigid development cycles.
The Agile Full-Stack Workflow: A Step-by-Step Breakdown

This is where things get practical. Let’s walk through the exact workflow your tech team follows.
6.1 Sprint Planning
This is where each new sprint begins. Everyone reviews the goals and requirements.
In this stage:
- Stakeholders share business needs
- Product Owner prioritizes features
- Developers estimate the effort
- The team decides what to build in this sprint
This meeting ensures everyone is on the same page before work begins.
6.2 Designing the Feature
Before writing any code, designers create:
- Wireframes
- User flows
- Screens
- Acceptance criteria
This ensures developers build exactly what stakeholders expect.
Stakeholders can review these designs easily—even without technical knowledge.
6.3 Development Phase
This is where full-stack developers bring the idea to life.
They work on:
- Frontend components
- Backend logic
- APIs
- Database structure
- Integration with other systems
There are also daily stand-up meetings—quick 10–15 minute sync calls where the team updates each other on progress.
6.4 Testing and QA
QA testers check:
- Functionality
- Speed
- User experience
- Bugs
- Performance
Testing is crucial—without it, small issues can turn into big failures later. Agile makes testing continuous, not delayed until the end.
6.5 Deployment
Once tested, the feature is moved to:
- Staging (test environment)
- Production (live environment)
Deployment is done carefully using automated pipelines to avoid downtime.
6.6 Sprint Review
This is where stakeholders get involved again. They see a live demo of features developed in the sprint. This is extremely important because:
- Stakeholders can give feedback quickly
- Developers can update features before moving forward
- Everyone stays aligned
This review minimizes surprises at the end of the project.
6.7 Sprint Retrospective
The dev team sits together to reflect:
- What went well
- What didn’t
- How to improve next time
This creates a culture of continuous improvement, which is the core of Agile software development.
What Non-Tech Stakeholders Should Focus On
You don’t have to understand coding—but you do need to understand processes. Here’s what to focus on:
- Business outcomes, not technical details
Don’t worry about code. Focus on how the feature will help users. - Prioritizing features smartly
Not all features need to be built immediately. - Giving timely feedback
Since Agile moves fast, delays in feedback slow the whole project. - Clarity in requirements
Provide clear expectations—preferably with examples. - Being available during reviews
Even 15 minutes of review per sprint can save weeks of rework.
Common Misunderstandings Non-Tech Stakeholders Have
Let’s clear some misconceptions.
- Misunderstanding 1: “Small changes should be quick.”
Even small changes often affect multiple layers—frontend, backend, and database. - Misunderstanding 2: “Design is separate from development.”
In Agile, design and development run side by side. - Misunderstanding 3: “Testing is optional.”
Without proper QA, failures can happen in real-time, affecting users. - Misunderstanding 4: “Developers know what I want.”
Developers know technology; only stakeholders know business goals. Good communication is key.
Tips for Smooth Collaboration Between Tech Teams & Stakeholders

Working smoothly together makes any project faster and easier. Here are some simple tips that help tech teams and non-tech stakeholders stay aligned:
- Use Simple Language
Everyone should speak in clear, easy words. Avoid technical terms and confusing jargon. The goal is to understand each other quickly. - Write Down Important Things
Whenever you discuss requirements, changes, or priorities, write them down. This prevents confusion later and keeps the whole team on the same page. - Make Quick Decisions
Agile works fast. If approvals or decisions take too long, the entire project slows down. Quick responses help the team keep moving. - Attend Sprint Demos
Sprint demos show you what the team has built. By attending them, you can see real progress and give feedback early. - Use Simple Agile Tools
Tools like Jira, Trello, Asana, or ClickUp help everyone track tasks and progress. They make communication easier and keep things organized.
Benefits of Agile Full-Stack Workflow for Businesses
Agile and full-stack development together create a powerful combination for modern companies. Here’s why this approach works so well:
- Faster Feature Delivery
Features are released quickly because the team works in short sprints. This means customers don’t have to wait long to see updates. - Lower Development Costs
Since work happens in small, iterative steps, teams can catch problems early. This prevents costly rework later. - Better Product-Market Fit
Continuous feedback helps the team understand what customers truly want. As a result, the product grows in the right direction. - High Transparency
Agile practices keep everyone informed. Stakeholders always know the progress, challenges, and next steps. - Reduced Risk
Issues are discovered early in the process rather than at the final stage. This makes the overall development more predictable and stable. - Easy Scalability
Full-stack teams can handle both front-end and back-end needs, allowing the product to scale smoothly as it grows.
Conclusion
Agile Development isn’t just for tech teams. It’s a Software Development Methodology designed to make collaboration easier for everyone—including non-tech stakeholders.
By breaking work into smaller steps, encouraging continuous feedback, and creating transparency, Agile software development helps reduce confusion and improves alignment.
Understanding the full-stack workflow empowers non-tech teams to:
- Ask the right questions
- Prioritize smarter
- Communicate better
- Participate actively
- Ensure the final product matches business goals
In short:
When both tech and non-tech teams understand each other, products become stronger, faster, and more impactful.


